In MySQL, temporary tablespaces are essential for managing non-compressed, user-created temporary tables as well as on-disk internal temporary tables. Understanding how to manage these tablespaces can help to prevent performance and disk space issues. The innodb_temp_data_file_path variable specifies the path, name, size, and properties of temporary data files.
Temporary tablespace data files can get rather big in contexts where temporary tables are often used. To reclaim disk space, restart the MySQL server, which will delete and restore the temporary tablespace data file.
To prevent excessive expanding, set the innodb_temp_data_file_path to a maximum file size.
First, use the following commands to determine if the temporary tablespace data file is autoextending. Login to MySQL and execute the command;
mysql> SELECT @@innodb_temp_data_file_path;Gets the current value of the MySQL system variable innodb_temp_data_file_path, which determines the location of InnoDB’s temporary data files. This variable specifies the location and format of the temporary tablespace files used by InnoDB. The results will be as displayed below.
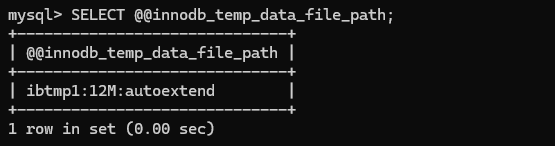
To find out the current size of the temporary tablespace data files, Use the command below to get the output as follows.
mysql> SELECT FILE_NAME, TABLESPACE_NAME, ENGINE, INITIAL_SIZE, TOTAL_EXTENTS*EXTENT_SIZE AS TotalSizeBytes, DATA_FREE, MAXIMUM_SIZE FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.FILES WHERE TABLESPACE_NAME = 'innodb_temporary'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
FILE_NAME: ./ibtmp1
TABLESPACE_NAME: innodb_temporary
ENGINE: InnoDB
INITIAL_SIZE: 12582912
TotalSizeBytes: 16105533440
DATA_FREE: 6291456
MAXIMUM_SIZE: NULLTotalSizeBytes indicates the current size of the temporary tablespace data file. Alternatively, we can also check the size of the temporary tablespace data file from the operating system. This file is normally created in the directory indicated by innodb_temp_data_file_path. If this configuration option is not explicitly set, the data file ibtmp1 is created in innodb_data_home_dir, which by default is the MySQL data directory.
To configure innodb_temp_data_file_path to specify a maximum file size.
Add the following line to the configuration file /etc/my.cnf .
[mysqld]
innodb_temp_data_file_path=ibtmp1:12M:autoextend:max:10240MRestart the MySQL service and check the value using the same command as before. The output will be as follows.
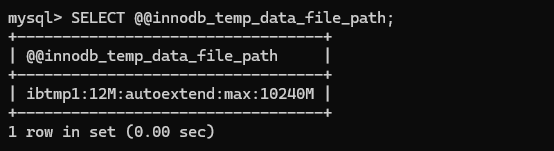
When the data file reaches its maximum size, queries fail and an error message appears to indicate that the table is full. To set the innodb_temp_data_file_path configuration value to default, restart the MySQL server.
Proper MySQL temporary tablespace management ensures that disk space is used efficiently and performance is optimized. By specifying the innodb_temp_data_file_path, you may keep temporary tablespaces from getting too big and avoid query failures. Maintaining a healthy MySQL system also includes restarting the server on a regular basis to recycle disk space and monitoring tablespace utilization.
For expert assistance on managing MySQL Temporary Tablespace efficiently, contact Skynats. Our team offers comprehensive support and tailored solutions to optimize your database performance, ensuring smooth and reliable operations. Reach out to Skynats today for professional guidance and support.

